VSCode
If you encounter problems during setup, please ask for help on discord
Initial project setup
Find your repository on the GitLab page of the course. It should be named like
mic-student-123Click on the blue
Codebutton on the top right and copy the URL displayed below "Clone with SSH"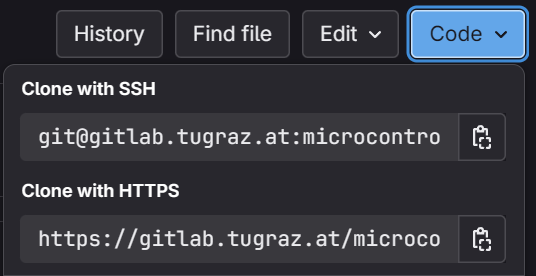
Open Visual Studio Code and select
View -> Command Palette...or pressCtrl + Shift + PType
Git: Clone (Recursive)and pressEnter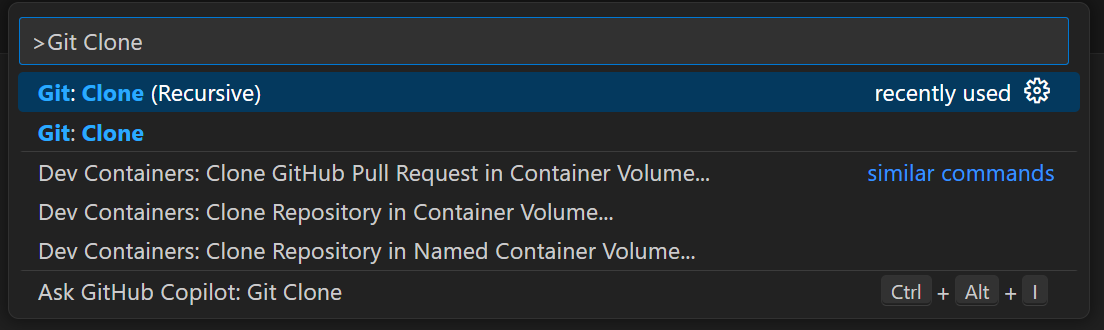
Paste the URL into the
Repository URLfield and press enter.
Select the directory where you want to store the repository. You will be asked to confirm trusting the host. Select
yes.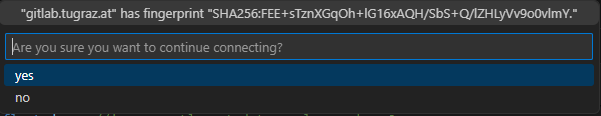
You will be asked to open the repository. Click on
Open. Confirm that you trust the authors of the project.The repository will be cloned and opened in Visual Studio Code.
If you are asked to install the recommended extensions, click on
Install All.Click on the

CMaketab on the left of the screen. and click onSelect a Kitnext to the[No Kit Selected]dropdown.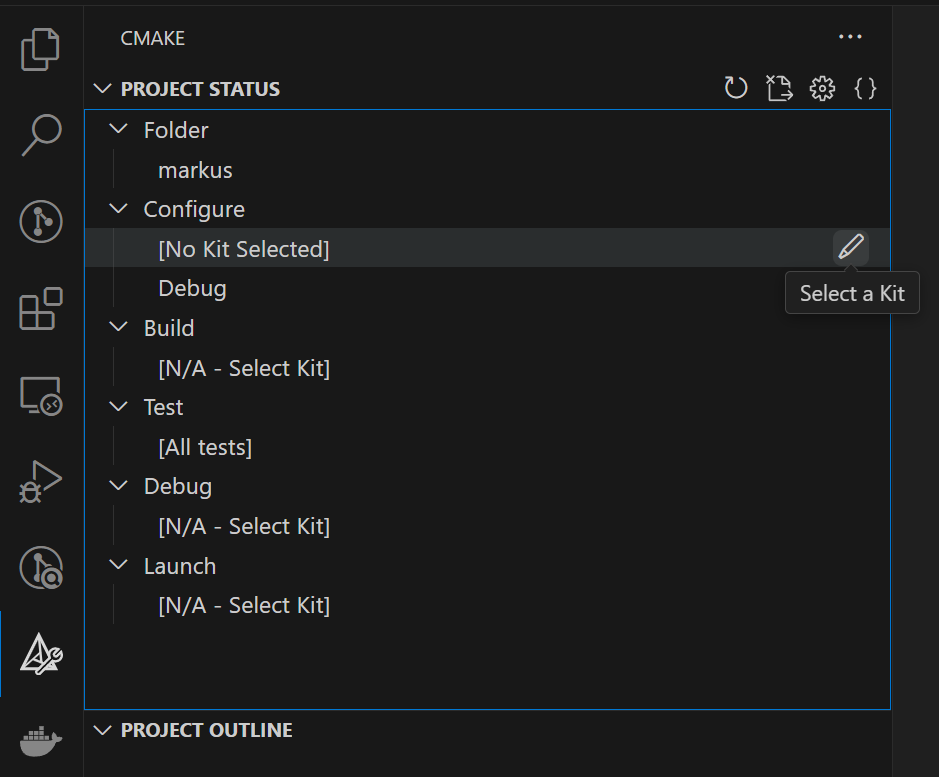
A kit can also be selected by pressing
Ctrl + Shift + Pand typingCMake: Select kitSelect
Pico ARM GCCfrom the list. CMake will now build the project.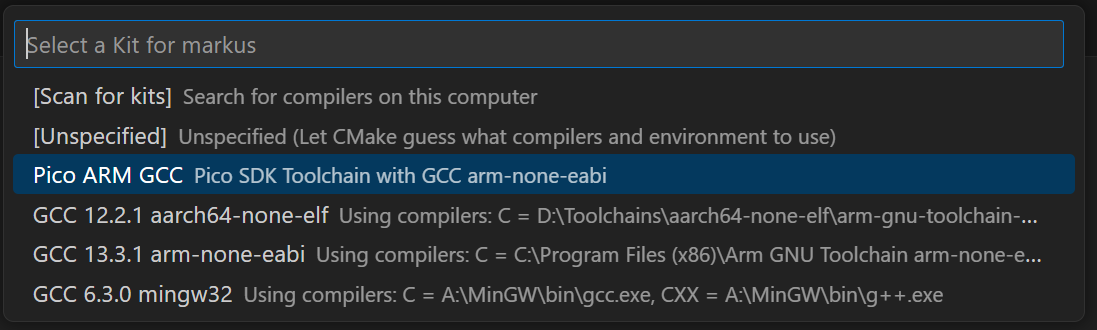
If you are not using Windows, open
.vscode/settings.jsonand change theopenocd_binarypath to the correct one for your system. The path should point to theopenocdexecutable in the.openocd/[arch]directory. Make sure that the binary is executable (runchmod +x openocdin the binary directory)On linux, please change line 11 of
.vscode/launch.jsonto"gdbPath": "gdb-multiarch"
Flashing and running
Click on the

Run and Debugtab on the left of the screen or pressCtrl + Shift + DSelect the
Pico Runconfiguration from the dropdown menu.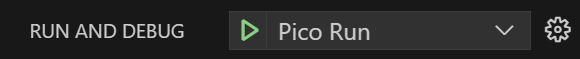
Press the green play button to build, flash and run your code. If you are asked to select a target, select the assignment you want to flash.
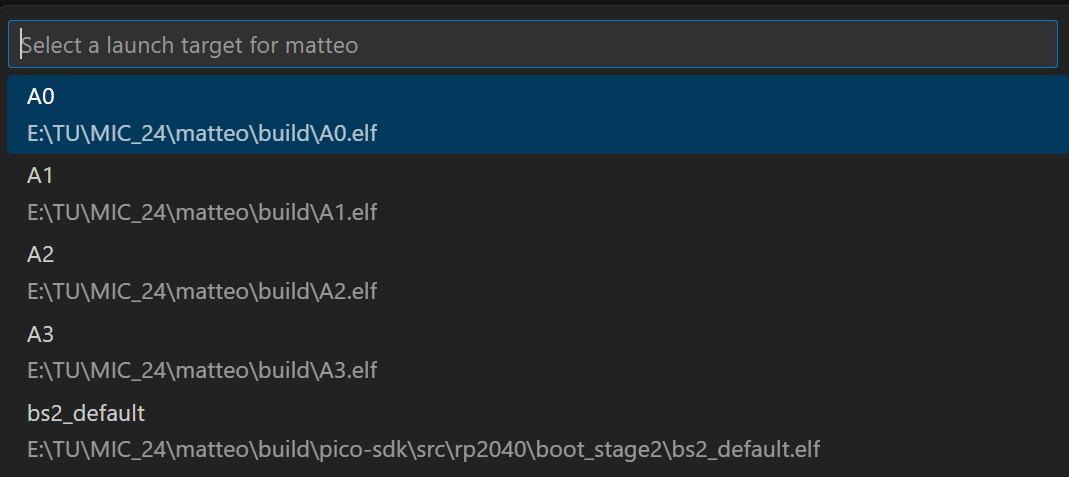
If you want to flash a different target, you can change the target in the

CMaketab. Select the target for Debug and Launch by clicking on the pencil icon next to the target.
To view the serial output of the board, you can click on the
Serial Monitortab at the bottom of the screen. Select the COM port of the Pico, modify the settings to match those in the image below and press onStart monitoring.
Debugging
Click on the

Run and Debugtab on the left of the screen or pressCtrl + Shift + DSelect the
Pico Debugconfiguration from the dropdown menu.
Press the green play button to build, flash and run your code. The debugger will start and halt your program. You can see the call stack and variables in the

Run and Debugtab.You can set breakpoints by clicking on the left side of the line number. The program will stop at the breakpoint and you can inspect the variables in the
Variablestab.To view the registers and their values, open the
XPERIPHERALSin the
Run and Debugtab.Use the debugger controls to step through the code, continue the execution or stop the debugging session. Hover over the buttons to see their function.

Debugging the hardware will be covered in assignment 0
Using the integrated Git
Committing and pushing changes
Click on the
Source Controltab on the left of the screen or pressCtrl + Shift + G.You will see a list of repositories and the changes you made. Ignore all repositories except your gitlab repository.
Enter a commit message which briefly describes the changes you made. Then press
Committo commit the changes.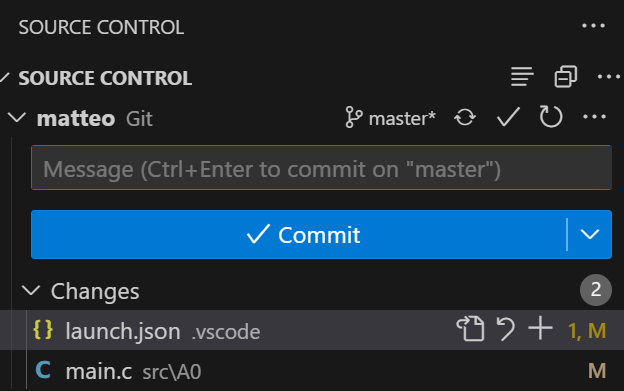
If you are asked to stage the changes, click on
AlwaysClick on
Sync Changesto push the changes to the server.
Creating a tag
Click on the
Source Controltab on the left of the screen or pressCtrl + Shift + G.Click on the three dots next to your GitLab repository and select
Create Tag...in theTagssubmenu.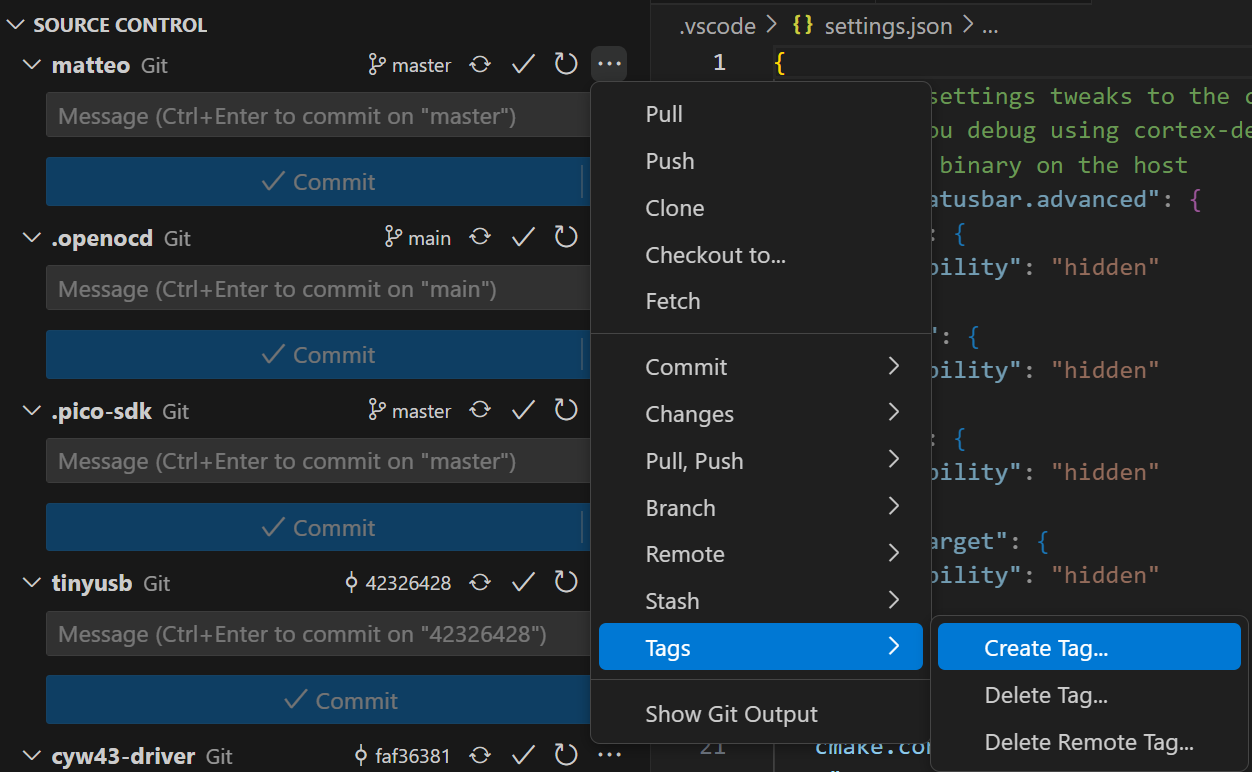
Enter a name for the tag and press
Enter. You can skip setting a message by pressingEnter.After creating the tag, you need to push it to the server. Press
Ctrl + Shift + Pand typeGit: Push Tagand pressEnter. Then select your repository and pressEnter.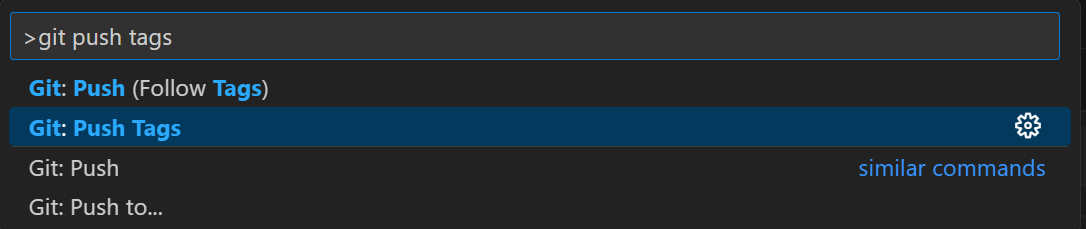
Your VSCode setup is complete! 🎉
You can now start working on the assignments.